



Upper left: View from trail 108 looking sourtheast over Val Salmurano.
Upper right: A goat on the way down from Rifugio Benigni.
Lower left: On trail 108 near Passo Salmurano, heading toward the canalone.
Lower right: Gentianella sp. common on the trail late summer.
Overview
Duration: 6 hours (Includes ~1 hour for lunch at Rifugio Benigni.)
Elevation: 1330 m (4364 ft) gain. High point at Cima Piazzotti at 2349 m (7707 ft)
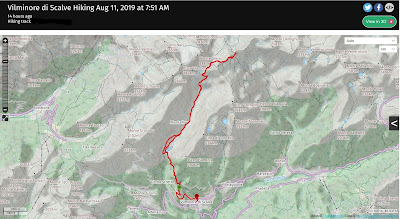
Location: Cusio, Alta Val Brembana, Bergamo, Lombardy, Italy
Hike Details
This was one of those hikes hatched over a Saturday morning coffee and hiked the next day, early on Sunday morning. That’s why we love Bergamo! The hike is described on the Club Alpino Italiano (CAI) Bergamo site as Sentiero 108. From Bergamo, you drive up Valle Brembana, forking left in the upper valley toward Olmo al Brembo, Santa Brigida, and finally reaching the little and very steep town of Cusio.
As you wind your way up through Cusio, you reach a point where you pay to use the road. Heading up hill there will be a little ticket machine on your right. We don’t remember the exact location, but you’ll know it when you see it. It costs 2 euros at time of writing this. After paying for a “ticket” you keep driving until you end up in a località called Sciocc at 1508 m where you can park near the trail head.
The first major thing you’ll see on the hike besides the beautiful scenery is the Casera Valletto at 1782 m. This is where we bought cheese and butter on the way down. See attached photo. wordreference.com translates casera as the bizarre but intriguing “cheese hut”. Treccani gives a more satisfying answer: a place in the mountains where dairy products are made from the milk produced during the summer by cattle grazing in the alpine pastures.



Left: Buying cheese and butter at Casera Valletto. Center: Hiking with goats along trail 108 to Rifugio Benigni. Right: Near start of hike on trail 108 - crossing a stream in Val Salmurano.



Left: Climbing the canalone on trail 108. Center: A view of Rifugio Benigni. Right: Heading up to Passo Salmurano.
After the canalone and a bit more scrambling here and there, you suddenly emerge on a flat spot at 2222 m where Rifugio Benigni sits at the head of Valle di Salmurano. The rifugio was inaugurated in 1984 with help from the Benigni family who intended to honor the memory of Cesare Benigni who died in 1981 on the nearby Pizzo del Diavolo di Tenda. From the rifugio you can look south upon the Alpi Orobie (also called the Bergamasque Alps) and north on the Central Alps (Wester Rhaetian Alps).



Left: A fresh baked dessert cooling off on the windowsill at Rifugio Benigni. Right: Another rifugio-made dessert - chocolate and coffee cake. Right: A main dish - piatto unico with polenta, spezzatino, funghi, fromaggio.
Via Mercatorum
On the way to or from the hike, take a moment (or more) to stop in Averara and see a part of the Via Mercatorum. The Via Mercatorum is a collection of medieval trade routes (think mule and foot paths) that connected Bergamo with the Val Valtelinna to the north.
One of the most beautiful parts of the Via Mercatorum is a porticoed passage in Averara. The modern road now passes parallel and lower so that the Via Mercatorum in Averara looks like a covered sidewalk. The most important businesses and people of the 15th and 16th centuries were present on the porticoed Via Mercatorum of Averara. Today, only frescoes and a few clues remain to suggest it.
The slow decline of the Via Mercatorum started in 1593 and the culprit was Venice. Bergamo had been under the dominion of Venice since 1428 and in the late 1500s, Venice was searching for new trade routes to connect Bergamo with Val Valtellina and beyond to its ally, the canton of Grisons in Switzerland. In 1593, the new route, Via Priula, was finished, named after the podestà of Bergamo, Alvise Priula who ordered its construction. At Olmo al Brembo, just south of Averara, the new route took a turn to the east to Piazzolo and Mezzoldo, therefore bypassing Averara.



Left and center: Views of the porticoed Via Mercatorum in Averara. Right: CAI map showing the network of trails and the location of Rifugio Benigni.
Flora
This hike is definitely all about the Euphrasia and Gentianella - at least by the abundance of these two plants. Euphrasia is a genus of about 450 species of herbaceous flowering plants in the family Orobanchaceae. They are semi-parasitic on grasses and other plants. And lo and behold, we tended to see Euphrasia growing in grass. The common name for Euphrasia is Eyebright referring to the plant's use in treating eye infections. Gentianella is a plant genus in the gentian family (Gentianaceae). We saw many purple type - likely one species. Unfortunately, with both plants, we can only identify down to the genus as we can’t figure out the exact species.
For more on flowers found around Bergamo, especially in the Bergamasque Alps, see our Pinterest page: Bergamasque Prealps Flowers and Plants. And our usual disclaimer: we use the resources listed in the post Resources for Identifying Plants around Bergamo to identify plants shown here. If we had to give ourselves a score for identifications, it would be 90% accurate for species and 95% for genus.
The plants are arranged below as follows:
[Family] Genus species – Common name in English (Common name in Italian)
[Apiaceae] Astrantia minor – Minor Masterwort (Astranzia minore)
![[Apiaceae] Astrantia minor – Minor Masterwort [Apiaceae] Astrantia minor – Minor Masterwort](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhXa_pAW0D1bPsdFPhexmjBOlslhyphenhyphenHpGIrGMNm3yinzvwah3HHPHA0no9kaFc96n81z0ydYmSE_HBmfH3oU0bcVO_GnTJTXE6dI9I2l5QoyTBnshknbpVGfazduElUIwHu6mDuc53Fx-ec/s400/%255BApiaceae%255D+Astrantia+minor.jpg)
[Asteraceae] Anthemis sp. Aromatic flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, closely related to Chamaemelum, and like that genus, known by the common name chamomile.
![[Asteraceae] Anthemis sp. [Asteraceae] Anthemis sp.](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgYlMyFctmMri8HyRe2ujyn_6KZ8QC24tEcTb8GyVnfbx1wMHwSVH4vs3VBCpjZKJMVsBnjNviTcP4aMUhiPIvowV5M5OMMy-_Oj46_XhK9dR8prPu8SQasnymS0EQqTr9ZmOjgpaht9co/s400/%255BAsteraceae%255D+Anthemis+sp.jpg)
[Asteraceae] Solidago sp. Probably S. virgaurea.
![[Asteraceae] Solidago sp. [Asteraceae] Solidago sp.](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgdUiEYYCOdgGGWAvLjqCJZbuFXIlKvlkpFVryoyavE6N6MWC2NUuNolsIovLtTYxbdCUxQ-dFuSWjvO5pltq9QTJXxNMZBcns2XMRUfHOtHva0Rj7HdeIZjt-e7jsy-DvtcC62xE7b_xA/s400/%255BAsteraceae%255D+Solidago.jpg)
[Celastraceae] Parnassia palustris - Marsh Grass of Parnassus (Parnassia delle paludi). We encountered lots of wet and seeping areas on this hike, perfect for this plant.
![[Celastraceae] Parnassia palustris - Marsh Grass of Parnassus [Celastraceae] Parnassia palustris - Marsh Grass of Parnassus](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEizIb6Tjh8ViK-YZ8fynup2PERKic4t4BMcVud-bz0On64zIfg9PrB3RWJMrOudw-OYnWfdzehx4KQu4jW-zPoejIbJ-zW-LRW7S3jMk1PMWWuEowYFEtZCkaq9m_xgE4aZG4u1aAR4fZA/s400/%255BCelastraceae%255D+Parnassia+palustris.jpg)
[Fabaceae] Trifolium alpinum – Mountain Clover (Trifoglio montano)
![[Fabaceae] Trifolium alpinum – Mountain Clover [Fabaceae] Trifolium alpinum – Mountain Clover](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiGj3rJWOB6x0UsYUe4ekgrfAhelvK_Yc3gFkmiED2Qpo26p-w3lrR_Z0l0Det1gB5ylHbXdoTG6gUoMjb-6wE1O1zqbBpYIg8gzWk0p1xOtAFXtMVmBr5b6QamXAJd-Ob8Q4hLWDdeiv4/s400/%255BFabaceae%255D+Trifolium+alpinum.jpg)
[Gentianaceae] Gentianella sp. – Gentian (Genzianella). Likely, G. campestris. One of the most common plant we saw on this hike beside Euphrasia.
![[Gentianaceae] Gentianella sp. [Gentianaceae] Gentianella sp.](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj1NzmvZvAozqrHg_uz2HTuEW21e0nLqNipFDHOL_LF5vz-9lqmwg6uB5XbkNDjlqMbPKfM-rocibZAbAIaZaxQv-KMhLzSgH6CTK6f2CKnGDG9fwtJi4MM8KgfZJp0F1kPvr0_V8cRw88/s400/%255BGentianaceae%255D+Gentianella+sp+%25281%2529.jpg)
![[Gentianaceae] Gentianella sp. [Gentianaceae] Gentianella sp.](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjiKRFRkuelxAYr5-NkTBqxK87LNq2D8QTFlgJ9r8jvWR-teBu_zl78AoVOzTkhWa-ENZyq1GLegUHm6b-Nq9NY4KbBvhV1ZeSLLWpk9juJgM4TI6EVSJejWEmidHIpkFvxtvb3rSOgKJc/s400/%255BGentianaceae%255D+Gentianella+sp+%25282%2529.jpg)
![[Gentianaceae] Gentianella sp. [Gentianaceae] Gentianella sp.](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjNLHEvbdgp3y7pAGGpSj0tqqxFWoWEivpcjvAkXWDoIjtua59I0KiI-2iGo7zK066QtISV26Vb6Y5Uf_PoonE75FyAxiOKtqDjpBa_xf7S-KZ6LflWTPd5_YvkLYNagBfpxIPJ624pFvs/s400/%255BGentianaceae%255D+Gentianella+sp+%25284%2529.jpg)
[Gentianaceae] Gentiana asclepiadea - Willow Gentian (Genziana di Esculapio)
![[Gentianaceae] Gentiana asclepiadea - Willow Gentian [Gentianaceae] Gentiana asclepiadea - Willow Gentian](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEi_NMEVqpX1x_nQcrcaaCSgHFVS0JHognXyCdctQdVoD28zCI0xTOXx_So-qyjRcJdPUa-ExcOG5JwJIbm9eqPzaXdVJcQD82SlEfuKwhwk2g6ufABJzAvylClZFtsN_UtTD1RxKemHZ0w/s400/%255BGentianaceae%255D+Gentiana+asclepiadea.jpg)
[Lamiaceae] Prunella vulgaris – Selfheal (Prunella comune)
![[Gentianaceae] Gentiana asclepiadea - Willow Gentian [Gentianaceae] Gentiana asclepiadea - Willow Gentian](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhiRUVa3C8Kj2h58g6vT0L2KCNFg5q_9c7UPDa9wlMQJ8xpN39HbVU4tClvmLTTy3aMcvpUXxqHfUWqr2eGePqwaHHhv1dSwynA8dX4LbwrKk-mnLfI0DlWf0bs_rfbewIRet9UN98j6s4/s400/%255BLamiaceae%255D+Prunella+vulgaris.jpg)
[Orobanchaceae] Euphrasia sp. – Alpine Eyebright (Eufrasia delle alpi)
![[Orobanchaceae] Euphrasia sp. – Alpine Eyebright [Orobanchaceae] Euphrasia sp. – Alpine Eyebright](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEg_pn1yKEqEouTdUW9AMJ6ItBq2QPs62zKm7TuMDnPzyhovso6m-w-ylNZ9hfGELNv1Pp4iAKZokmtclGJpyae-HwKFTXE4ZpZ_3rSusn7LNWtqymz1tka-hPobaOS2pN22h4g-Hx9eyPM/s400/%255BOrobanchaceae%255D+Veronica+sp+%25281%2529.jpg)
![[Orobanchaceae] Euphrasia sp. – Alpine Eyebright [Orobanchaceae] Euphrasia sp. – Alpine Eyebright](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgXFehEvi5cji6Kf4ZQKUIdRXgvk-AlshAH0ujt0zYQRx6ZrtDWQ1I2KgCPYRsqBq-YTQodQ5RPyQy10aRaomklN_ie4-Q4rZCYagOP3MyyypNK_J986GfbzRV_H-zJULyVFhzXjKC4tZw/s400/%255BOrobanchaceae%255D+Veronica+sp+%25282%2529.jpg)
[Papaveraceae] Pseudofumaria lutea – Yellow Corydalis (Colombina gialla)
![[Papaveraceae] Pseudofumaria lutea – Yellow Corydalis [Papaveraceae] Pseudofumaria lutea – Yellow Corydalis](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEg0Sh9q1CqLJPhMJKhC-KEKKjUE10qzNby52Tgyt_bHH2jTK7nIfn2VVxMjJiBvxQYzuzAhDc5GZLELe-qjl0ZixVK0D1BnYwOWtrOTdhujrf878Xy9wl54qQ4R5GM3yz8fY-DJjYzvZbw/s400/%255BPapaveraceae%255D+Pseudofumaria+lutea.jpg)
[Ranunculaceae] Aconitum lycoctonum – Wolfsbane (Aconito lupaia)
(no photo)
[Ranunculaceae] Aconitum napellus – Monk’s-Hood (Aconito napello)
![[Ranuculaceae] Aconitum napellus – Monk’s-Hood [Ranuculaceae] Aconitum napellus – Monk’s-Hood](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgacIQzz8Ksor3q354fo7tdyqmdroDAxTe3z6_Wj9Ih-41FyGUXytX5TNplsDfSiUc94ik3oBD-ovU0YL4GK_9NeCS7wpA0h8RZOeMf8tS2HwYWP5uHHSoLadbzVPE_wkISqhYOq9Ssl_s/s400/%255BRanuculaceae%255D+Aconitum+napellus+%25281%2529.jpg)
![[Ranuculaceae] Aconitum napellus – Monk’s-Hood [Ranuculaceae] Aconitum napellus – Monk’s-Hood](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhXmNCtD2JjCaFABfuZN-Z2WTMMnhGiVr9rwx1H1u5kZYR23TTKH-A4N6gHcYN-jgkCD-9mna4e07RvHZNrKjQm-LMfto-U4GLcgZI_m8C1i5eqHD4TzCnzeylbpvV-TMVLQKaxJne_QM8/s400/%255BRanuculaceae%255D+Aconitum+napellus+%25282%2529.jpg)
![[Ranuculaceae] Aconitum napellus – Monk’s-Hood [Ranuculaceae] Aconitum napellus – Monk’s-Hood](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEheECwkTtAK34uhHWyNKiOs_UG4ECaLqnocPyF29kLu7HgzgrQ-rdpEeaVC2ZXMSBjeA4If4qTlKekUdX2KrdLuh-Kw-Tzqf_VwyE0AoUl58coOGuZEtJVv9_RQVgJ0fbMU-yewnk-qGO0/s400/%255BRanuculaceae%255D+Aconitum+napellus+%25283%2529.jpg)
Views from the Trail


Left: Lago Piazzotti - near Rifugio Benigni. Right: View south toward dark forms of Torrione S Giacomo.

Panorama from Cima Piazzotti - view north over Lago Zancone and Lago di Trono.

Panorama from near Rifugio Benigni looking south.


Left: Saved GPS tracks from Cusio to Rifugio Benigni. Right: Hike profile details.

Signage at Passo Salmurano.
















![[Amaryllidaceae] Allium schoenoprasum – Wild Chives (Erba cipollina) [Amaryllidaceae] Allium schoenoprasum – Wild Chives (Erba cipollina)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhnmZchCBlK110l088fvE9TZBQC5G4uUNaSMcePdy691jzMIuZYx8-DkseZNN6tZlhCwboFa6Vu1_xHbbJ9PDqKfJNAuIVZVkkUI0IHDY-6OrDOcEKX376hPh3yfH6BbMW3KtswELMnFs8/s400/%255BAmaryllidaceae%255D+Allium+schoenoprasum+%25282%2529.jpg)
![[Amaryllidaceae] Allium schoenoprasum – Wild Chives (Erba cipollina) [Amaryllidaceae] Allium schoenoprasum – Wild Chives (Erba cipollina)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhNBVrlVa05Rj8oT6hsmeKzG1cMiC-1j0dLsZx781brrMcFuutjo4Pa_pW9zleh3jTDvroZJFYx1YYTXx55ZiCep6-kl3c7c8n3ai2YzjqlamCQFcCLLu361l3tgrFwH44qqzVB6JlqDZ0/s400/%255BAmaryllidaceae%255D+Allium+schoenoprasum.jpg)
![[Apiaceae] Bupleurum petraeum – Rock Hare’s Ear (Bupleuro delle rocce) [Apiaceae] Bupleurum petraeum – Rock Hare’s Ear (Bupleuro delle rocce)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiJnfAI66makFglYRwLYGe0U9WSpWTdK-bPhgTJ8gmGM73F3AHF0Pz1j13Pc0a_6nh5dtFgK2Y1d_BVtD9P-Kb9B47Gn8Ol9KYlxUJ26IDXdhai44GfI9agOR9a6RVO20bibxGXvui_3bA/s400/%255BApiaceae%255D+Bupleurum+petraeum+%25282%2529.jpg)
![[Apiaceae] Bupleurum petraeum – Rock Hare’s Ear (Bupleuro delle rocce) [Apiaceae] Bupleurum petraeum – Rock Hare’s Ear (Bupleuro delle rocce)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEi_dSMjcaehejsbJsvr7hq27qWFvKV39SYU58UPKboOtshEizJBWIv52NPnKShLljSkeIPqj7eKmHrTx_wIeFkXJsYKcz7IBMyXpK9pEzyY9VbfJaUsEZmF5Iqct8vfn-aDiSYC0MHzmHE/s400/%255BApiaceae%255D+Bupleurum+petraeum.jpg)
![[Asteraceae] Carlina sp. [Asteraceae] Carlina sp.](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiofOuiU_Vgs4J4JbXyWRRxyKsS7M_ZffWO3h1A38wgh0YEXICEzkIxSwNj21sykkwn318q9l4XprvDN-azELEyys44CNzNaqA6vdoXfLdj0vzzor9dB4WOMesS9srWu-Q8ImaXCa2mIs8/s400/%255BAsteraceae%255D+Carlina.jpg)
![[Asteraceae] Centaurea uniflora - Plume Knapweed (Fiordaliso alpino con un capolino) [Asteraceae] Centaurea uniflora - Plume Knapweed (Fiordaliso alpino con un capolino)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgAEWfz9CLR9w4p6FEWyWvrRWCYOs0QEA-6tpLRKlKpN_E-z-s2T-Ga2ctaEUpbBBqrRWviqAV1FRaKtzeKLrehOA8Pdd8zDxC6tUkqJZlB-DvZgJKH-gfxn0AK2Oefi-bzjK84pDR13hg/s400/%255BAsteraceae%255D+Centaurea+uniflora.jpg)
![[Asteraceae] Cirsium erisithales – Yellow Thistle (Cardo zampa d'orso) [Asteraceae] Cirsium erisithales – Yellow Thistle (Cardo zampa d'orso)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEijdg-A8MZZ9xxwq37xvKj88MzqaYw1d-z5eOTsEYMh5IuiF7dJZCeL1pEbmz88gf4RHMJzWtubgxQ-k90__NrtkFhor8YNfpo8BxuYN_DWdB_c_BEE5ra5onAedXDHH6SmkWdlm1pi0uo/s400/%255BAsteraceae%255D+Cirsium+erisithales.jpg)
![[Asteraceae] Cirsium spinosissimum - Spiniest Thistle (Cardo spinosissimo) [Asteraceae] Cirsium spinosissimum - Spiniest Thistle (Cardo spinosissimo)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhcNojY-dLR1m8lqN15aVZWDbT-yf2J48XogDaWZDH-0HJTLd3x7hL9AAc4rVvB1LubidlJkqLWZfZjlvjU8PRMWLsIY2rXdrL6KwrnVPDVqFNxYcjjTsl9Bj7-TlVW7FBAQyGTbVqDP_U/s400/%255BAsteraceae%255D+Cirsium+spinosissimum.jpg)
![[Asteraceae] Crespis aurea – Golden Hawk's Beard (Radicchiella aranciata) [Asteraceae] Crespis aurea – Golden Hawk's Beard (Radicchiella aranciata)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjYITScofvh1B_xqKo11aFQJRl09u-_mJbEd69opmRdJ7Wm9glNpRJMw06L4tPyNPnWUx-xh8UaaacpDx0KV4Ex22eqjsldzJsd9h3rM4cTM_wJR7SJDwadQ13nDG5c59LhDJOyg3IMy10/s400/%255BAsteraceae%255D+Crespis+aurea.jpg)
![[Asteraceae] Leontopodium sp. – Edelweiss (Stella alpina) [Asteraceae] Leontopodium sp. – Edelweiss (Stella alpina)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjGOIVmG6jqT6HvpmA2nWv2sCm0JyeHdjorYSVddmeTCbLfupfwCW_-Bi0MvR0G_xLctggdwqZJ9t1DGbQErQ28LUeAmYpyciKLVRKBJn4yz_6DsGubhklbQZinh5OuKHAiWdzxckR4I2c/s400/%255BAsteraceae%255D+Leontopodium.jpg)
![[Boraginaceae] Eritrichum nanum – Arctic Alpine Forget-me-Not (Eritrichio nano) [Boraginaceae] Eritrichum nanum – Arctic Alpine Forget-me-Not (Eritrichio nano)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEh8p9gEB5kI8VXA9jlLiSk8NrqqmryZsmC2gat_ey9lIjakwZmWC0CuCX_tHZSOiVPNdybZhoeW_bkWbR3ibRqr8JU9P6T9QTH80Zk6VsaGUrdVi2WYQF737ygoAVJFNvEjuOV791qUtQA/s400/%255BBoraginaceae%255D+Eritrichum+nanum+2.jpg)
![[Boraginaceae] Eritrichum nanum – Arctic Alpine Forget-me-Not (Eritrichio nano) [Boraginaceae] Eritrichum nanum – Arctic Alpine Forget-me-Not (Eritrichio nano)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiMplRDhpLLW00p2C7iGxLrf306qTKaexPLBCoBOJtGThlhtlM-d0SByHJYqmYqERivNjs4Yy3HiArX5r_Awj9Z8zPJIcJZWHngMNVfq4jm-ob02jmZ5UjEKkweiWPh3eQU1D8zXUtrsXA/s400/%255BBoraginaceae%255D+Eritrichum+nanum.jpg)
![[Brassicaceae] Noccaea rotundifolium – Round Leaved Penny Cress (Erba storna a foglie rotunda) [Brassicaceae] Noccaea rotundifolium – Round Leaved Penny Cress (Erba storna a foglie rotunda)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgzT5TcVNdQbt9jZ9R2tsontLSsvIm2vpLQpAQWiMcOWvbShN_OpUYZBkhHNh_tNwnujtlsuSqdx2l5ZbBtw4_XwEz958AKaMSycNJXfPIHfy2rL8ihfUmcIVbEnPe60K7GWISJGA0K6Ws/s400/%255BBrassicaceae%255D+Noccaea+rotundifolium.jpg)
![[Caryophyllaceae] Cerastium arvense – Filed Chickweed (Peverina dei campi) [Caryophyllaceae] Cerastium arvense – Filed Chickweed (Peverina dei campi)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEi8ciMKUmhf_qtIKUEvE1Kp0YdFBE4DoGLvH2QKIjX5mRJaJe-f-Sr3wCyk0TF-F851e7FlGbD-NQxxoDDlqw0FbBrEcnm18hyKVfyGMeldr0GRxV5xCppqxlL9K2589MNAkQftA3c-iD0/s400/%255BCaryophyllaceae%255D+Cerastium+arvense+2.jpg)
![[Caryophyllaceae] Cerastium arvense – Filed Chickweed (Peverina dei campi) [Caryophyllaceae] Cerastium arvense – Filed Chickweed (Peverina dei campi)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEg_luPnLIBiNcGKUNMMS-TJvmJ4Xfl9ac4lBRgH7TGN6sPkIa_nsT3Ue5tOftpqMlNHVkDMvfKIKA9gdHuhCF1-NloXfTM7tDHovtXcyfxBow8RzQh50HNCdgwdq7mxLK-WuDUdUVeGyvY/s400/%255BCaryophyllaceae%255D+Cerastium+arvense.jpg)
![[Caryophyllaceae] Dianthus sp. [Caryophyllaceae] Dianthus sp.](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEg133FMN3hUenz0FMwIstotL_CLcYpMwSC_VAQmw4QPqsp1rRfTZdK2Qoa77uBCzx0l3hHoDhZDFo8YqLN06ZD-5cn72n_hrgzELu81o7CeKihngEdd-W_Xd4WDNVjbRQ3JFgSa392E1Gw/s400/%255BCaryophyllaceae%255D+Dianthus+sp..jpg)
![[Caryophyllaceae] Dianthus superbus – Fringed Pink (Garofano superbo) [Caryophyllaceae] Dianthus superbus – Fringed Pink (Garofano superbo)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhK9ZY84trkaquZwuDIE9mpaj4BD053fRsdZUYIrR1Mr3ktG92oaAkboKo4qrY8PG_XUVI5sigCBuU5JsZ7tl3LZtKyJeQ4tapjBKOfpFcm3ySNI91qkm5J9KISzzyO0RWDT1BD_Wh22_U/s400/%255BCaryophyllaceae%255D+Dianthus+superbus.jpg)
![[Caryophyllaceae] Saponaria officinalis – Bouncingbet, Common Soapwort (Saponaria comune) [Caryophyllaceae] Saponaria officinalis – Bouncingbet, Common Soapwort (Saponaria comune)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiu2gUtw2PLA84TW1e9Somj6FimoN6qiDXpadtG3PrJdYwQuaLCQ_xSO-Gwx130WOh3xZrtapOoUO9bf8zZ8e5eeEkbg60QcsCzr3FrMlR6bVd58ueM-ann3UyEP7UJ81CNVGnppgdh6L0/s400/%255BCaryophyllaceae%255D+Saponaria+officinalis.jpg)
![[Celastraceae] Parnassia palustris - Marsh Grass of Parnassus (Parnassia delle paludi) [Celastraceae] Parnassia palustris - Marsh Grass of Parnassus (Parnassia delle paludi)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhWitAYox6L660IoqzZSrS5AlWI7ekSatukmNew5aR_RZUfr1otlDEEIyns-rVbMqsuEOTsGRoaXtkQg70V0-VcazrLUHhLRDzRV1L5N-Ako4pMmXtiivmtCu2jFQXsM4PyTEJveKrRQO4/s400/%255BCelastraceae%255D+Parnassia+palustris.jpg)
![[Crassulaceae] Rhodiola rosea – Roseroot Stonecrop (Rodiola rosea) [Crassulaceae] Rhodiola rosea – Roseroot Stonecrop (Rodiola rosea)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgXFMVtt1YT6ugvgiDWzps0mEZJcouAOjaJAj5-OHkkRee69RUNJj6guFPFfzsxiSzycvRYjAL3Avi7eb2ec7G-TdrNYamy9s-LXtu2vBtGfEavgqY4X5Orh3v5ABXDseqJQv_OnBqQB3I/s400/%255BCrassulaceae%255D+Rhodiola+rosea+2.jpg)
![[Crassulaceae] Rhodiola rosea – Roseroot Stonecrop (Rodiola rosea) [Crassulaceae] Rhodiola rosea – Roseroot Stonecrop (Rodiola rosea)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhxrHd-H9Ie_z-CsKKTgkFIZLIi4KGyAXsu0-T7v4ptv5mooaLA_SZYjZ3_GLFavj8t9PjRgzrSQg2JJu3a-Zq7-4-Ohn9nvEvPyXmCha0wML4q8bHr7FNVtxZkyN9tsPF0qkO-ByBd6KY/s400/%255BCrassulaceae%255D+Rhodiola+rosea.jpg)
![[Crassulaceae] Sempervivium sp. – Mountain Houseleek (Semprevivo), possibly S. montanum [Crassulaceae] Sempervivium sp. – Mountain Houseleek (Semprevivo), possibly S. montanum](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhOSZxoEeacA0y4Tdw38QF3CKUvGikGUmJUzDZmpSYfkqv-01a77bz_clHWVYzU4ktrYOXOE27IqzbfH1NuEJXyoEIwCI-8tPXIXIjaGO2Hnbk1taqSCdX30ltY6CQCCEibSTeC15k5kOE/s400/%255BCrassulaceae%255D+Sempervivium+sp.jpg)
![[Gentianaceae] Gentian sp. – Gentian (Genziana) [Gentianaceae] Gentian sp. – Gentian (Genziana)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhptI7wPPpM0KWhmTz92e8iexJ2BALDJyxRw7VP0KT6frAqdGoBaLs7NMjgHAXYOcT_tAfzDoITCtWmAepBMCXMmYFnf67nETkcWCNSM5DAxrWsLn6BdUW3TFLdyxfqlIb4uABGA35-dKw/s400/%255BGentianaceae%255D+Gentian+sp.jpg)
![[Orobanchaceae] Pedicularis sp. – Lousewort (Pediculare) – possibly P. kerneri. [Orobanchaceae] Pedicularis sp. – Lousewort (Pediculare) – possibly P. kerneri.](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhgWw18GB2reYz70NOQnOjyJ2MRhEAB7y-QdwvtcZtz0eAyWGdqpWrMz0fT_23F4rvlZ-ViJ3B1hiG5VO2DFEczbX0_2YuxK_aMHWpovbfIN91_rEDr_nEa-lxJYc9EcIUZKlXv2FQmxqg/s400/%255BOrobanchaceae%255D+Pedicularis+sp.jpg)
![[Orobanchaceae] Rhinanthus sp. - Yellow Rattle (Cresta di gallo) [Orobanchaceae] Rhinanthus sp. - Yellow Rattle (Cresta di gallo)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgPPVxhZJoSsa5dOS5UyeKvPEPrRIC5uOkTbaUFPZqtL1ThpoCuVQJUsTluyMEWu6j7XeVAQCFJF74rFmxymwaY6wBOzil9Ivv0sTQKCk6F1suNH026q6XbexkK7sW3S4r4QpolfsgOZEY/s400/%255BOrobanchaceae%255D+Rhinanthus+sp.jpg)
![[Plantaginaceae] Veronica sp. – Alpine Eyebright (Eufrasia delle alpi) [Plantaginaceae] Veronica sp. – Alpine Eyebright (Eufrasia delle alpi)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiqTlKtkGgxOQpuKEQpsiUHE7dcmnr9erH-Yb_d2EAQ6IY8JgwHumtCUyJJiAnWjg4ldvTN9yRN87R2HpzFCwuwNMowOWQ3Aaw8Zyr-t5DgXWee0g-ps-5zM-ukxXvSzfH5f37nLCjsUd4/s400/%255BOrobanchaceae%255D+Veronica+sp.jpg)
![[Papaveraceae] Pseudofumaria lutea – Yellow Corydalis (Colombina gialla) [Papaveraceae] Pseudofumaria lutea – Yellow Corydalis (Colombina gialla)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEggT__DVdZFoZM42cCtykGFnNoF2nG32ZKyjlfkXnsk053KzcOVBIoFXoGpO5uo_zpsK3z3XZkYU5bMoLsbqbGKjONQSBqNjw1LIj5IOydVQ9GGtCjakWy4KFJau3O3F-JOa25sAutFLUM/s400/%255BPapaveraceae%255D+Pseudofumaria+lutea.jpg)
![[Plantaginaceae] Linaria alpina – Alpine Toadflax (Linajola alpina) [Plantaginaceae] Linaria alpina – Alpine Toadflax (Linajola alpina)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhjwQ5qUk_XVP1lhqKOdFenYZ-EcRzF9xfKMs3Ox0EXclrQSD3mU3EAz2R3Vb5xeo1U-8KQW0jNgC-KMZwukAiX0lYFpWoDps2VaP40GSr5GqErbhkSI7v4mTXV4Lpin2X-KoUmZLeqyY8/s400/%255BPlantaginaceae%255D+Linaria+alpina+2.jpg)
![[Plantaginaceae] Linaria alpina – Alpine Toadflax (Linajola alpina) [Plantaginaceae] Linaria alpina – Alpine Toadflax (Linajola alpina)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEh84iMqO8M8EkVIPb36AtT5wBxxbhAsWw4NohS8-6AtRLjy_1014ARpqyCp9NgursNPHuNKujlZRyxDhH6QCPoqxT-M0STEjgKXYWGoImCMxgLMMSQ5_oyio4Kd7A88PtmzfH3r7uwDSKo/s400/%255BPlantaginaceae%255D+Linaria+alpina.jpg)
![[Plumbaginaceae] Armeria alpina – Alpine Thrift (Spillone alpino) [Plumbaginaceae] Armeria alpina – Alpine Thrift (Spillone alpino)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEi7JfLT476fehjra3YobiuGepUkKILA8tcgmg7Ojf4AUjI-ZmMg0eJ4MgRiVDOjah7bF0GsDbPj5Geceg4DYhZ-VSYs9UtMVaQQvxTOA6UhBuL3FY7dZrhd6RUod_hzi8ouJ9qfT_49X_g/s400/%255BPlumbaginaceae%255D+Aermeria+alpina+2.jpg)
![[Plumbaginaceae] Armeria alpina – Alpine Thrift (Spillone alpino) [Plumbaginaceae] Armeria alpina – Alpine Thrift (Spillone alpino)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEinhokznptSfJTIvZuLwhgyNnUoWpzO4PUEYUss70urJBybvmp534krMSlXn9q7R4VXZQw3b6NGeTCA7wnriv1kJ0OR2RwHUHAJ6NTXUJnudDYv-Ox3Solq2lZDKnhO-tQFfGnrEll4Zng/s400/%255BPlumbaginaceae%255D+Aermeria+alpina+3.jpg)
![[Plumbaginaceae] Armeria alpina – Alpine Thrift (Spillone alpino) [Plumbaginaceae] Armeria alpina – Alpine Thrift (Spillone alpino)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjprBf7QQrYJyywx8D9b0j5lBHrK5GdajOrEUx7Zs7Q5Ul0Qx0_OBgDblO4yaZH8ec0k2sgMREaltnd3MszjXViM009xmDKFD6Q1QMuzKdZqrtfr432L125GSWsh9CfBMF7sKMJeiPfk9Y/s400/%255BPlumbaginaceae%255D+Aermeria+alpina.jpg)
![[Rosaceae] Potentilla nitida – Pink cinquefoil (Cinquefoglia delle Dolomiti) [Rosaceae] Potentilla nitida – Pink cinquefoil (Cinquefoglia delle Dolomiti)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgHQqrYw9Y0OFXRwNDTE-EJ32C9z-YKE7j4C4yf3bCtJSLQEvetoM8hG5tGhHZ72E03qjMVWPIV_ZILL5rkWVM-3Xtcvm3J-2afqp8iXNhljGaKvf_DofPYeqi9JmPydwm7ALVuTZeFfXY/s400/%255BRosaceae%255D+Potentilla+nitida.jpg)
![[Rosaceae] Sanguisorba dodecandra – Italian Burnet (Salvastrella con dodici stami) [Rosaceae] Sanguisorba dodecandra – Italian Burnet (Salvastrella con dodici stami)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEh9pKR5m7rNGhCct4mP0_w4ZPmhDdEMGnCTqCF5lA5NnICXNHE4l-UcD3oBR69FICrhKmG6uqXHo1gKOozzkXCLWpIs3ffkBBrtX5xLDgS0LR0fyGtva_iMZeRgVnDS4d8ue0mQoMjsDmA/s400/%255BRosaceae%255D+Sanguisorba+dodecandra.jpg)
![[Ranunculaceae] Pulsatilla alpina – Alpine Pasqueflower (Pulsatilla alpina) [Ranunculaceae] Pulsatilla alpina – Alpine Pasqueflower (Pulsatilla alpina)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhqkIdbRURT8VSyibvAGvDYvLgWdliqlX0rbYBOoc1nGkDEWqdaFl5SJjlBQenYQf3fBSkQdm2GdO5FowBQ3u-_zBe347CKz14tiVOaoUKM_KacNQ3I9-WHSO3OEIo2p01ALOz35m8xlZM/s400/%255BRanunculaceae%255D+Pulsatilla+alpina+2.jpg)
![[Ranunculaceae] Pulsatilla alpina – Alpine Pasqueflower (Pulsatilla alpina) [Ranunculaceae] Pulsatilla alpina – Alpine Pasqueflower (Pulsatilla alpina)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhSg0H1DpMDN8d-oFup6bHs77ElMWfaK4Tr5MDthakrMsRoSdZwv2Yrcg7y7zME9TVzqYVYyw9ihxJRLIe8uwuJZFf8d-nSxOECkWQI6_s0LUmXF8YsFs-KjpBg6XzGjN1UC9k4E-k0I3Y/s400/%255BRanunculaceae%255D+Pulsatilla+alpina.jpg)
![[Saxifragaceae] Saxifraga aizoides – Yellow Saxifrage (Sassifraga gialla) [Saxifragaceae] Saxifraga aizoides – Yellow Saxifrage (Sassifraga gialla)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEijAWt6C0LOsX744jK28xrfhXdr3NNYFt_cHxQj7pV11OlOqfisOPWeWf1XDZWDW_SEUe91wGVQPfBzR7w64SdHg6NUk1xRCSdSdhVgb2goDmdkLPEpYRLZEVYnnmF71oqYV674OsZZ6Vo/s400/%255BSaxifragaceae%255D+Saxifraga+aizoides.jpg)
![[Saxifragaceae] Saxifraga byroides – Mossy Saxifrage (Sassifraga briode) [Saxifragaceae] Saxifraga byroides – Mossy Saxifrage (Sassifraga briode)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhVHm34SgQkiZRx8YpX9JEXXau3jRvpPI1beK1hRSsS1_aA7HscJ8AZwQl3h8s6jArKzJ0pzoWfb4-699Ursk_T5qc-2hX-YlnrQ8O-nYTF0vu4sBwBVtkpuYNFjSHPKES8d8aLhJRCpeA/s400/%255BSaxifragaceae%255D+Saxifraga+byrodes.jpg)
![[Saxifragaceae] Saxifraga byroides – Mossy Saxifrage (Sassifraga briode) [Saxifragaceae] Saxifraga byroides – Mossy Saxifrage (Sassifraga briode)](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjcW4ikcm3lW_6qv82HdVGP2ReONB5G6nNJHAfHAGK8EShrAq_4K1uJYlvApss8tAnRvkut8-rQ37_RwGEA0trTeXigTxB9SWbws-P04slcg1nqCU1WRlqzkNU_YuuuN0Ie78Yzo_ALMls/s400/%255BSaxifragaceae%255D+Saxifraga+byroides+2.jpg)











