Overview
Diagram Showing Build Process
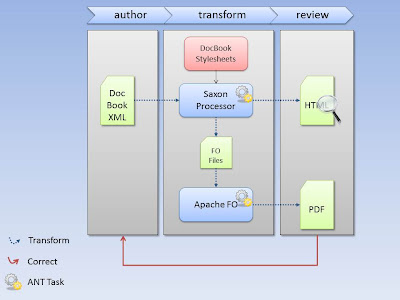
This post is about simple, single source publishing using DocBook, that is, starting with DocBook XML markup you can transform it into other formats (like HTML and PDF) using freely available tools. DocBook is a common markup language for producing documentation.
Disclaimer: If you are serious about single source publishing using DocBook then what we show here is probably not for you ultimately. Rather, you'll want robust DocBook authoring tools like the the ones given here: DocBook Authoring Tools. We've had lots of experience with one of these tools, Oxygen XML Editor, and can say that after preparing this post we can appreciate what goes into it and tools like it are worth the money.
Should you keep reading? Keep reading if you are interested in playing around with DocBook to see what it is and how you use it, and you are moderately savvy around installing and running things on your computer. The goal of this post is to show a simple build process workflow for building DocBook into other output formats using free tools.
Motivation: Our original intent was to take the output from this blog (an RSS or Atom feed) and convert that to DocBook and then from there convert to whatever format we wanted like HTML, PDF, or epub. But before we can achieve that lofty goal we needed to step back and look at the simpler problem of transforming simple DocBook content into other formats. There are other sites, such as at vogella.com and cuddletech.com, that show this. So what do we add here? Here, we try to focus on a workflow that makes sense in addition to showing the tools that enable it. The basic workflow is this: author, transform, review, and repeat.
The project we develop here can be downloaded here.
Tools and Libraries Used
- Eclipse
- What is it?
- Eclipse is a free toolset for software development.
- Why use it?
- It's free and easy to get. It has basic XML editing capabilities as well as many plugins you can get to help out with development and other tasks. For example, you can use the Vex editor for working with DocBook. Vex has command completion, but what we found is after a while working with DocBook you have pretty good idea of what tags go where.
- Eclipse as an organizing principle of your workflow is a good concept since you can keep everything together in a project. With a project, sharing or moving the project is relatively easy using importing and exporting paradigms.
- Also, ANT (a Java build tool) is built into Eclipse which makes developing a build process workflow easier. And, ANT tasks can be run at the command line for more flexibility.
- What is it?
- Saxon.
- What is it?
- Saxon is a collection of tools for processing XML documents like DocBook source files.
- Why use it?
- There is a Saxon-HE - Home Edition that is free to use.
- In our tests, it turned out to be flexible and have the least amount of things to download and assemble. There are just two JAR files to download. (Only one is really needed.)
- It also was able to deal with XInclude which is a approach for merging many XML documents into one. XInclude allows you to include the contents of one XML document in another. In this post we use many XML files in a hierarchical arrangement to represent the source content. Again, it’s about workflow, so the ability to deal with many XML files was important. For more on processing modular documents, see the Sagehill book Chapter 23. Modular DocBook files.
- Other options? We tried out the XSLT library and it worked, but Saxon seemed easier to use - just one JAR. We did not try Xalan.
- What is it?
- Apache FO.
- What is it?
- Apache FOP http://xmlgraphics.apache.org/fop/ (Formatting Objects Processor) is software that can be used to process an intermediate stage of the transformation of DocBook markup to PDF. The intermediate stage are XSL formatting objects (XSL-FO) a markup language for paged media.
- Why use it?
- There doesn't seem like much else is available that is free.
- What is it?
- DocBook Stylesheets
- What are they?
- We are transforming XML documents using XSL stylesheets (used in an XSLT engine like Saxon) to our desired output. The stylesheets are the instructions for performing the transformation. They stylesheets we'll use in this post are the ones that transform our source markup to HTML and to FO (formatting objects).
- Why use them?
- Required: these are the transforms. We downloaded them from Sourceforge and used docbook-xsl-doc-1.77.1.zip.
- What are they?
- DocBook DTD
- What is it?
- The DocBook DTD defines how DocBook markup must be written.
- Why use it?
- Required: the rules of the road in regard to DocBook. We downloaded from www.oasis-open.org at http://www.oasis-open.org/docbook/xml/4.5/. We used version 4.5. You don't have to have the DTD local to your project, but it helps if you are working offline. The examples shown here assume the DTD is local.
- What is it?
We tried hard to use DocBook 5 but couldn't get it to work properly and ended up using DocBook 4.5. We followed the transition guide to make that leap from V4.X to V5.0 but little problems kept arising when we tried to put all the tools we mention above together. We suspect that it should be easy to move to V5.0 and we'll try to look at that in the future.
Example DocBook File Directory Structure
So let's say we are going to produce a best-of this blog's posts for the last three years. In this case one strategy for organizing the content would be to have a chapter for every year and keep the content of each year in a separate file. A master "book.xml" file will manage the ordering of the separate entries. So our files might look like this:
book.xml
entry1.xml
entry2.xml
entry3.xml
…
In book.xml we would have the (simplified) markup:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no"?>
<!DOCTYPE book PUBLIC "-//OASIS//DTD DocBook XML V4.5//EN" "../lib/docbook-xml/docbookx.dtd" [
<!ENTITY % myent SYSTEM "entities.ent"> %myent;
]>
<book>
<bookinfo>
<title>Travelmarx DocBook Example</title>
<author>
<firstname>Travelmarx Blog</firstname>
<affiliation>
<address>
<email>&email;</email>
</address>
</affiliation>
</author>
<copyright><year>2012</year> <holder>Travelmarx</holder></copyright>
<abstract>
<para>Selected Travelmarx posts.</para>
</abstract>
</bookinfo>
<chapter id="chapter2012">
<title>2012 Posts</title>
<para>Interesting posts from 2012.</para>
<xi:include xmlns:xi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XInclude" href="entry1.xml"/>
<xi:include xmlns:xi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XInclude" href="entry2.xml"/>
<xi:include xmlns:xi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XInclude" href="entry3.xml"/>
</chapter>
<chapter id="chapter2011">
<title>2011 Posts</title>
<xi:include xmlns:xi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XInclude" href="entry4.xml"/>
</chapter>
</book>
Setting Up the Eclipse Project
Here's the order we are going to do things:
- Create a Java project in Eclipse.
- Create folders to help organize how we'll author and build.
- Copy the Saxon JARS into the project and modify the build path of the project.
- Copy the Apache FO Library into the project and modify the build path of the project.
- Copy the DocBook stylesheets into the project and use them in book.xml.
- Create DocBook source files.
- Create a build file.
- Run a build.
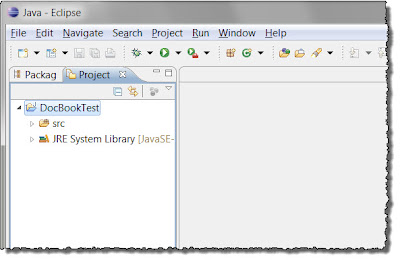
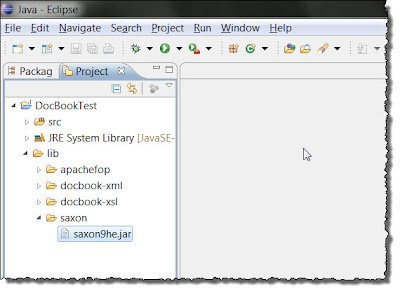
Basic Project Setup
After Step 2 (left) and After Step 7 (right) in Setup
1. Create a new workspace, for example, workspace_travelmarx, or use an existing.
2. Create new Java Project.
3. Set view to Project Explorer if needed.
4. Create a new folder \lib\saxon and put saxon9he.jar here.
5. Create a new folder \lib\apachefo and put all the contents of the Apache FOP (1.1) distribution files here. Not all of it is needed, but it's easier to just copy it all for now.
6. Create a new folder \lib\docbook-xsl and put all the DocBook XSL files from the ZIP here.
7. Create a new folder \lib\docbook-xml and put all the DocBook DTD files from the ZIP here.
8. Create a new folder \input, \output, and \css. The input folder will contain source DocBook files. The output folder will contain transformed output. The \css folder will contain optional style sheets for HTML. You don't have to put anything here. We generated a css file by viewing source of this blog and grabbing the style. Not perfect, but a start.
9. Create a new folder \tmp. This will be a temporary staging area. In the transformation from DocBook to PDF there is an intermediate stage in the form of Formatting Objects (FO). This directory contains the intermediate FO files.
Create DocBook Source Files
Book.xml File in Markup (left) and Book.xml file and Related Files (right)
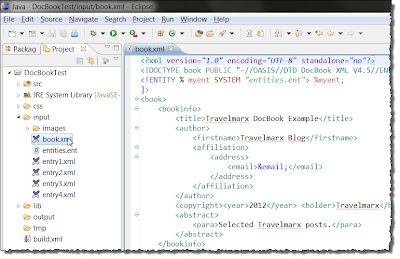
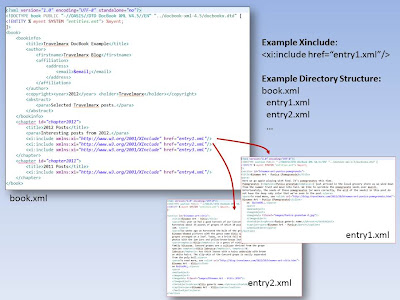
1. All of the source input is in the \input folder and all the following folders and files should be created inside this folder.
2. Create an \images folder. We want to include images so we'll put them here.
3. Create book.xml. Using book.xml is a convention. The build.xml script below expects book.xml.
4. Create entry1.xml, entry2.xml, entry3.xml, and entry4.xml. This arrangement of book.xml to entry files is arbitrary. You can select what you want.
5. Create entities.ent. This file contains data (reusable text) that can be used in any file that declares an ENTITY that references the entities.ent file. It is one way centralize common text.
Build
Instead of building the build.xml file piece by piece, we’ll show the completed file. It has the following pieces:
- Property definitions
- MacroDef - macro definition to run the saxon transform
- TaskDef - task definition to run the ApachE FO transform to get final PDF
- Targets that define what action you want to perform. For example, there are tasks for building HTML and one for building the PDF.
The build.xml file has a default target, build HTML.
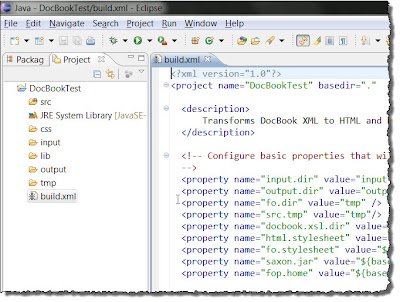
Build.xml Markup (left) and Running Build.xml at the Command Line (right)
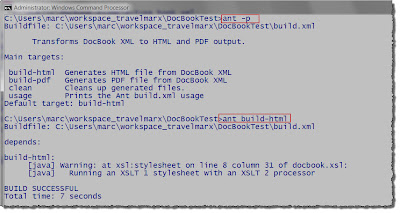
Run the build.xml File
1. Select the build.xml and Run As, Ant Build (without the ellipsis) to run the default target. Or, select the Ant Build with the ellipsis to change the target.
2. Use shortcut keys, Alt+Shift+X, Q
3. Or, if the build file is what is open, click the Run icon or use the Run menu.
4. Or, run it from the command line.
The output of the HTML or the PDF is in the \output folder. Here is the build.xml file:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<project name="DocBookTest" basedir="." default="build-html">
<description>
Transforms DocBook XML to HTML and PDF output.
</description>
<!-- Configure basic properties that will be used in the file.
-->
<property name="input.dir" value="input" />
<property name="output.dir" value="output" />
<property name="fo.dir" value="tmp" />
<property name="src.tmp" value="tmp"/>
<property name="docbook.xsl.dir" value="${basedir}/lib/docbook-xsl" />
<property name="html.stylesheet" value="${docbook.xsl.dir}/html/docbook.xsl" />
<property name="fo.stylesheet" value="${docbook.xsl.dir}/fo/docbook.xsl" />
<property name="saxon.jar" value="${basedir}/lib/saxon/saxon9he.jar"/>
<property name="fop.home" value="${basedir}/lib/apachefop"/>
<macrodef name="saxon">
<attribute name="in" />
<attribute name="out" />
<attribute name="style" />
<attribute name="classpath" default="${saxon.jar}" />
<element name="params" optional="true" implicit="true" />
<sequential>
<java classname="net.sf.saxon.Transform"
classpath="@{classpath}">
<arg value="-s:@{in}" />
<arg value="-xsl:@{style}" />
<arg value="-o:@{out}" />
<arg value="-xi:on"/>
<arg value="html.stylesheet=css/master.css"/>
<params />
</java>
</sequential>
</macrodef>
<taskdef name="fop" classname="org.apache.fop.tools.anttasks.Fop">
<classpath>
<fileset dir="${fop.home}/lib">
<include name="*.jar"/>
</fileset>
<fileset dir="${fop.home}/build">
<include name="*.jar"/>
</fileset>
</classpath>
</taskdef>
<!--
- target: usage
-->
<target name="usage" description="Prints the Ant build.xml usage">
<echo message="Use -projecthelp to get a list of the available targets." />
</target>
<!--
- target: clean
-->
<target name="clean" description="Cleans up generated files.">
<delete dir="${output.dir}" />
</target>
<!--
- target: depends
-->
<target name="depends">
<mkdir dir="${output.dir}" />
</target>
<target name="xinclude">
<xsl.xinclude in="${input.dir}/book.xml" out="${src.tmp}/book.xml" />
</target>
<!-- target: build-html
-->
<target name="build-html" depends="depends" description="Generates HTML file from DocBook XML">
<delete>
<fileset dir="${output.dir}" includes="*"/>
</delete>
<saxon in="${input.dir}\book.xml"
out="${output.dir}\book.html"
style="${html.stylesheet}"/>
<!-- Copy the stylesheet to the same directory as the HTML files -->
<copy todir="${output.dir}/css">
<fileset dir="css">
<include name="*.*" />
</fileset>
</copy>
<!-- Copy images to the same directory as the HTML files -->
<copy todir="${output.dir}/images">
<fileset dir="${input.dir}/images">
<include name="*.*" />
</fileset>
</copy>
</target>
<!-- target: build-pdf
-->
<target name="build-pdf" depends="depends" description="Generates PDF file from DocBook XML">
<delete quiet="true">
<fileset dir="${fo.dir}" includes="*"/>
<fileset dir="${fo.dir}/images" includes="*"/>
</delete>
<saxon in="${input.dir}\book.xml"
out="${fo.dir}\book.fo"
style="${fo.stylesheet}"/>
<!-- Copy images -->
<copy todir="${fo.dir}/images">
<fileset dir="${input.dir}/images">
<include name="*.*" />
</fileset>
</copy>
<fop format="application/pdf"
basedir="${fo.dir}"
fofile="${fo.dir}\book.fo"
outfile="${output.dir}\book.pdf"/>
</target>
</project>








































